Data Labeling | Web Scraping Tool | ScrapeStorm
Abstract:Data Labeling refers to the process of adding "correct information (labels)" to training data for machine learning and artificial intelligence. ScrapeStormFree Download
ScrapeStorm is a powerful, no-programming, easy-to-use artificial intelligence web scraping tool.
Introduction
Data Labeling refers to the process of adding “correct information (labels)” to training data for machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Applicable Scene
Data labeling has a wide range of applications. In the medical field, it assists diagnosis by annotating abnormal areas in CT scan images; in the field of autonomous driving, it is used to provide identification information of objects such as vehicles, people, and traffic lights in camera images. In natural language processing fields such as chatbots and SNS analysis, large amounts of text need to be annotated to identify customer intentions and emotions. In addition, it is used in speech recognition to identify the speaker’s speech and emotions; in video analysis, it is used to identify actions and behaviors; in addition, it is used for motion analysis and anomaly detection of surveillance cameras.
Pros: The biggest advantage of data labeling is that it can significantly improve the accuracy of AI learning. Accurate and consistent label information can improve the reliability of learning data, thereby building more practical models. In addition, the participation of people with expertise can generate effective labeled data even in areas that require advanced judgment. In addition, labeled data can be used as an asset for other projects and future re-learning, which is extremely valuable for long-term AI strategies.
Cons: On the other hand, the disadvantage of data labeling is that it is costly and time-consuming. Especially when dealing with large amounts of data, the workload of manual labeling is huge, and the labor cost cannot be ignored. In addition, if the quality of labeling is uneven, the accuracy of the model may decrease, or even learning bias may occur. In addition, labeling work usually requires expertise, and securing the right people is also a challenge. Although the introduction of automatic labeling technology can partially alleviate the burden, it cannot completely replace manual labeling.
Legend
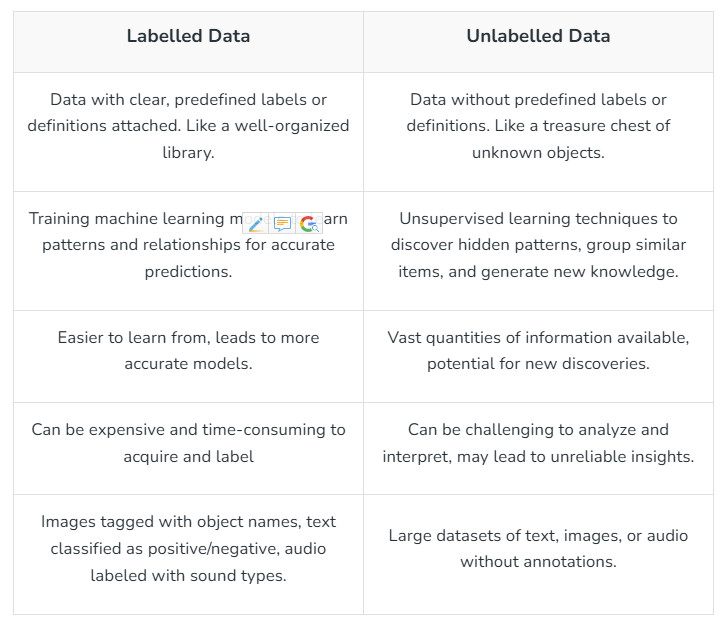
1. Labeled and unlabeled data.
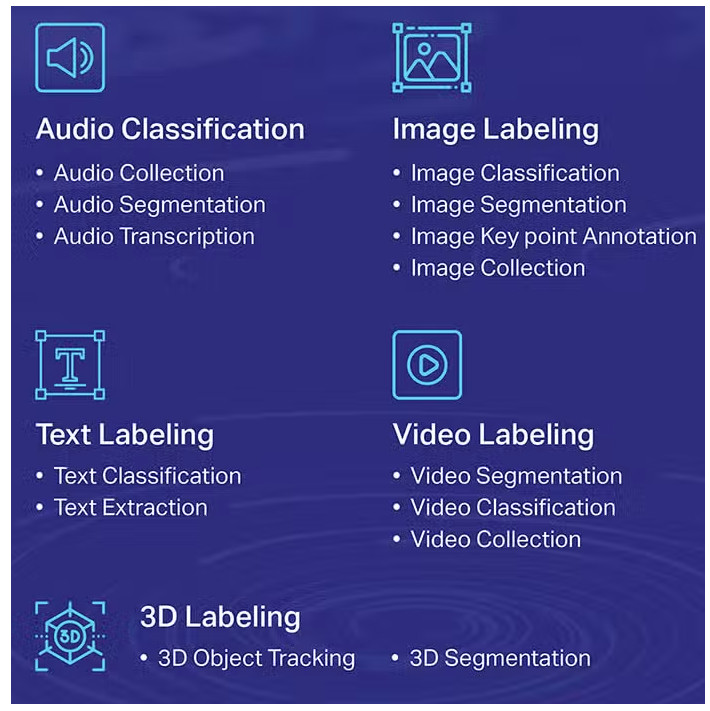
2. Data Labeling type.