Solar Radiation | Web Scraping Tool | ScrapeStorm
Abstract:Solar Radiation refers to the total energy released by the sun that propagates through space in the form of electromagnetic waves and ultimately reaches the Earth. ScrapeStormFree Download
ScrapeStorm is a powerful, no-programming, easy-to-use artificial intelligence web scraping tool.
Introduction
Solar Radiation refers to the total energy released by the sun that propagates through space in the form of electromagnetic waves and ultimately reaches the Earth. It primarily consists of visible light, infrared radiation, and ultraviolet radiation, playing a fundamental role in the Earth’s climate system, energy cycle, and ecosystem maintenance. As solar radiation passes through the atmosphere, it undergoes absorption, scattering, and reflection before reaching the Earth’s surface, where a portion of its energy heats the surface and drives natural phenomena such as evaporation, convection, and wind formation.
Applicable Scene
Solar radiation is widely used in meteorology and climatology to study surface temperature variations, seasonal changes, and the formation of climatic zones, serving as an indispensable key factor. In the renewable energy sector, it is extensively applied in the design and performance evaluation of solar photovoltaic power generation and solar thermal utilization systems. Additionally, in agriculture, it is used for crop growth prediction and photosynthetic efficiency assessment; in architecture and urban planning, it supports energy-efficient building design and mitigation of urban heat island effects through solar analysis.
Pros: Solar radiation is a clean energy source that remains stable on a global scale, with no risk of depletion and minimal environmental impact, which is its most significant advantage. Furthermore, with advancements in observational technologies and numerical models, solar radiation can now be quantified with relatively high precision for applications in climate prediction and energy planning.
Cons: Solar radiation is significantly influenced by atmospheric conditions, cloud cover, latitude, seasons, and diurnal variations, resulting in considerable instability in energy supply and analytical outcomes. Additionally, intense ultraviolet radiation can pose risks to human health and ecosystems, necessitating thorough assessment and the implementation of appropriate protective measures during practical utilization.
Legend
1. A visible-spectrum solar radiation image captured from the ground.

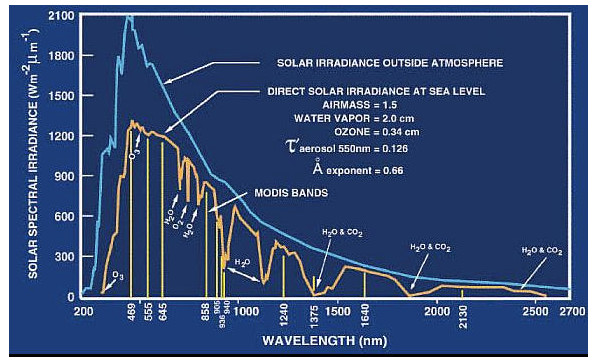
2. Comparison diagram of solar radiation spectra between the Earth’s surface and the top layer of the Earth’s atmosphere.
Related Article
Reference Link
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solar_irradiance
https://www.iberdrola.com/social-commitment/solar-radiation
https://ugc.berkeley.edu/background-content/solar-radiation/