Direct Solar Radiation | Web Scraping Tool | ScrapeStorm
Abstract:Direct solar radiation refers to the parallel rays of sunlight that reach the Earth's surface without being scattered by the atmosphere. Its intensity is jointly determined by factors such as the solar elevation angle, atmospheric transparency, cloud cover, and altitude. ScrapeStormFree Download
ScrapeStorm is a powerful, no-programming, easy-to-use artificial intelligence web scraping tool.
Introduction
Direct solar radiation refers to the parallel rays of sunlight that reach the Earth’s surface without being scattered by the atmosphere. Its intensity is jointly determined by factors such as the solar elevation angle, atmospheric transparency, cloud cover, and altitude. The solar elevation angle directly influences the amount of direct solar radiation by altering the atmospheric optical mass along the radiation’s propagation path (e.g., the atmospheric optical mass number is smallest at noon, resulting in the strongest radiation). Atmospheric transparency is inversely correlated with water vapor and dust content; higher transparency leads to less radiation attenuation. Cloud cover significantly blocks radiation, with thick cloud layers capable of completely obscuring direct solar radiation. As altitude increases, the radiation path shortens, reducing atmospheric absorption, which explains why regions at high altitudes (such as the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau) receive significantly stronger direct solar radiation than plains at the same latitude.
Applicable Scene
Direct solar radiation is most intense in clear, dry regions at high altitudes with excellent atmospheric transparency (e.g., plateaus and deserts), serving as a critical parameter for solar energy utilization, climate research, and agricultural assessment of light and heat resources.
Pros: Direct solar radiation offers high energy intensity and stability under clear atmospheric conditions, enabling efficient solar energy collection and precise climate/agricultural modeling with minimal atmospheric interference.
Cons: Its availability is highly weather-dependent (e.g., blocked by clouds) and geographically limited to arid/high-altitude regions, posing challenges for consistent energy supply in humid or low-lying areas.
Legend
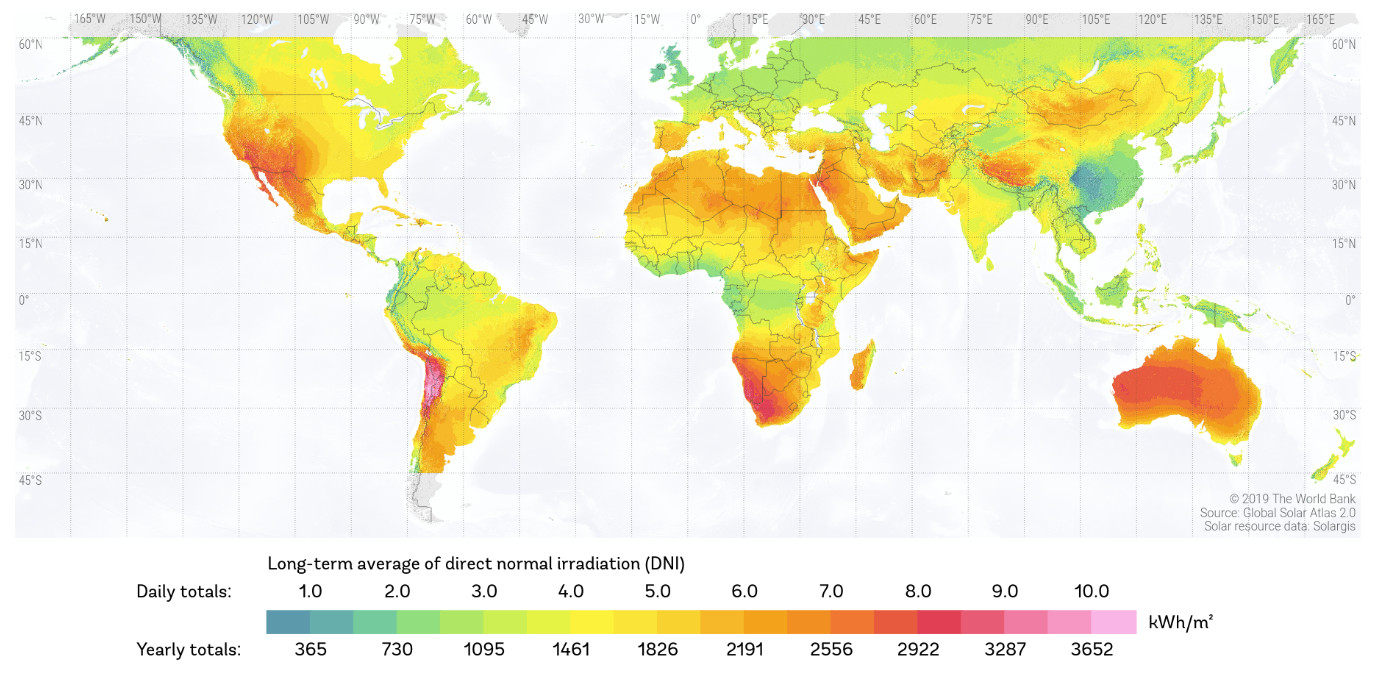
1. Direct Solar Radiation.
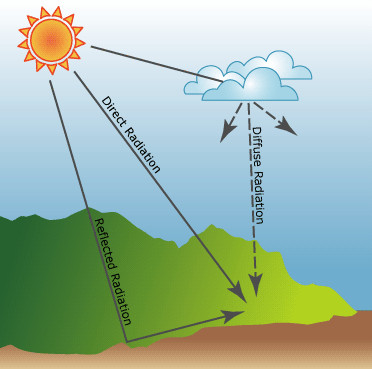
2. Global Map of Direct Normal Radiation.