Net Radiation | Web Scraping Tool | ScrapeStorm
Abstract:Net radiation refers to the difference between all incoming radiation energy received by the Earth's surface and the radiation energy emitted from it. ScrapeStormFree Download
ScrapeStorm is a powerful, no-programming, easy-to-use artificial intelligence web scraping tool.
Introduction
Net radiation refers to the difference between all incoming radiation energy received by the Earth’s surface and the radiation energy emitted from it. It serves as a core indicator in meteorology and surface energy balance. Typically calculated by combining the incoming and reflected amounts of shortwave radiation from the sun with the net exchange of longwave radiation between the surface and the atmosphere, net radiation is expressed in watts per square meter (W/m²). It directly governs the heating and cooling of the Earth’s surface and functions as the energy source for various surface processes such as evapotranspiration, sensible and latent heat fluxes, and ground heat storage.
Applicable Scene
Net radiation is widely utilized across fields such as meteorology, agricultural meteorology, land surface process studies, environmental engineering, and climate change research. In agriculture, it serves as foundational data for estimating crop evapotranspiration and planning irrigation, making it indispensable for evaluating crop growth environments. In meteorology and climate science, it is used to analyze surface energy balance and understand temperature changes and the formation of local climates. Additionally, in urban environmental studies, it is applied to assess the urban heat island effect and analyze the impact of surface materials. In remote sensing, it is also used to estimate large-scale net radiation distributions based on satellite data.
Pros: The primary advantage of net radiation lies in its ability to directly represent the “effective energy input” at the Earth’s surface, enabling comprehensive assessment of complex surface processes. By treating shortwave and longwave radiation as an integrated system, it clearly captures the physical basis of evapotranspiration and surface temperature changes. Moreover, it can be estimated not only from ground-based observations but also from satellite data, allowing for large-scale and continuous monitoring and thereby contributing to improved reliability in climate analysis and environmental assessment.
Cons: Accurate calculation of net radiation involves multiple factors such as surface albedo, temperature, and atmospheric conditions, making it susceptible to observation and estimation errors. It is particularly sensitive to cloud cover and aerosols, leading to significant temporal and spatial variability. Consequently, data from a single location or a short time frame may be insufficient to fully assess surface conditions. Furthermore, net radiation alone only indicates the total energy amount; understanding its distribution into sensible heat, latent heat, and ground heat fluxes requires the integration of other observational data.
Legend
1. Net radiation and temperature.
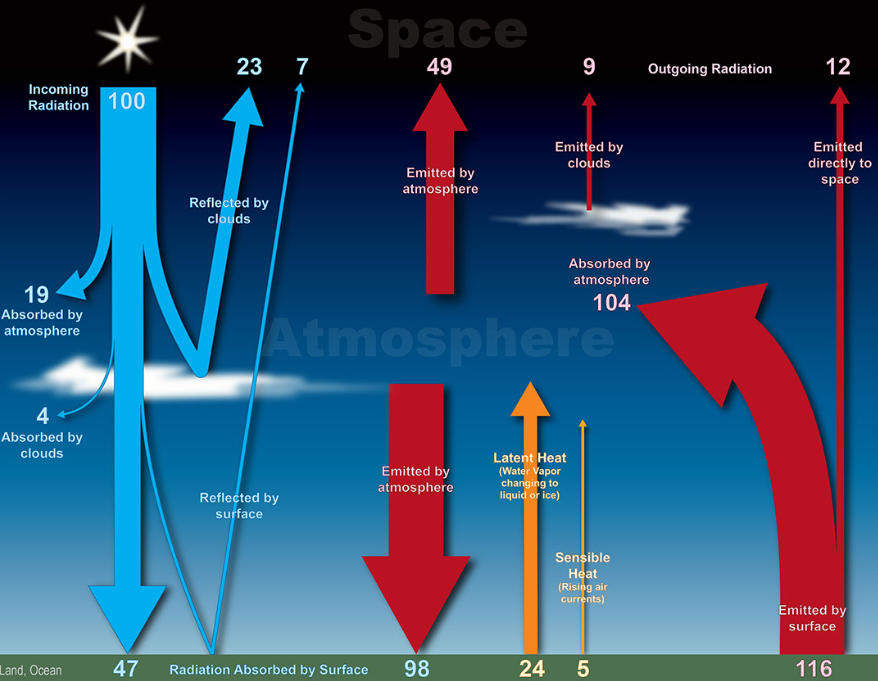
2. Diagram of a net radiometer.
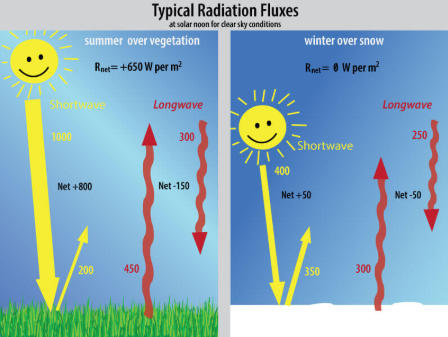
Related Article
Reference Link
https://science.nasa.gov/earth/earth-observatory/global-maps/net-radiation/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/physics-and-astronomy/net-radiation
https://wikifire.wsl.ch/tiki-indexfe48.html?page=Net+radiation