Data Consistency | Web Scraping Tool | ScrapeStorm
Abstract:Data consistency refers to ensuring that multiple copies or related data remain the same or comply with specific rules at different nodes and time points in a distributed system, database or data storage scenario, and ensuring that the data still accurately reflects the business logic and actual situation after various operations (such as reading, writing, updating, and deleting). ScrapeStormFree Download
ScrapeStorm is a powerful, no-programming, easy-to-use artificial intelligence web scraping tool.
Introduction
Data consistency refers to ensuring that multiple copies or related data remain the same or comply with specific rules at different nodes and time points in a distributed system, database or data storage scenario, and ensuring that the data still accurately reflects the business logic and actual situation after various operations (such as reading, writing, updating, and deleting).
Applicable Scene
It is suitable for scenarios with extremely high requirements for data accuracy and reliability, such as multi-node distributed database systems, cloud storage services for cross-regional data synchronization, financial transaction systems (such as bank transfers that require account balance data to be consistent on multiple servers), and e-commerce inventory management systems (to avoid overselling and ensure real-time and accurate inventory data).
Pros: Ensure the correct execution of business logic, such as data consistency in financial transactions to avoid financial losses; improve system reliability and reduce failures caused by inconsistent data; enhance user experience, so that the data obtained by users is always accurate and reliable.
Cons: The implementation is complex and requires additional mechanisms (such as distributed locks and transaction coordination) to ensure consistency, which increases system complexity and development costs. It may affect system performance. For example, if strong consistency is required, it is necessary to wait for confirmation from multiple nodes, resulting in increased operation delays. In distributed systems, complete consistency is difficult to achieve and a trade-off must be made between consistency and availability.
Legend
1. Data Consistency.
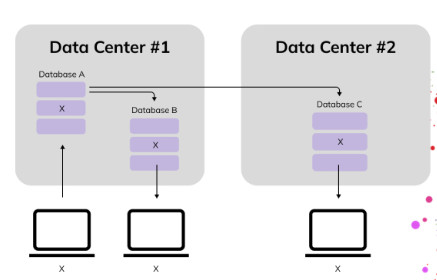
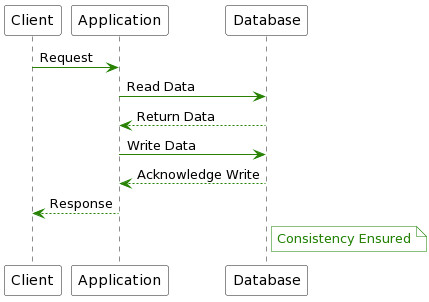
2. Data Consistency.
Related Article
Reference Link
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/data-consistency-vs-data-integrity