Relative Humidity (RH) | Web Scraping Tool | ScrapeStorm
Abstract: ScrapeStormFree Download
ScrapeStorm is a powerful, no-programming, easy-to-use artificial intelligence web scraping tool.
Introduction
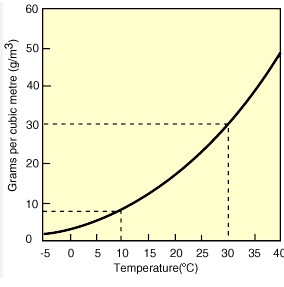
Relative humidity (RH) is a commonly used metric in meteorology to measure the humidity of air. It refers to the ratio of the actual water vapor pressure in the air to the saturation water vapor pressure at the same temperature, usually expressed as a percentage. In other words, it reflects the relationship between the water vapor content in the air and the maximum amount of water vapor it can hold at that temperature. For example, when the water vapor content in the air reaches its saturation point, the relative humidity is 100%, and the air is considered “saturated.” At this point, dew, fog, or precipitation is very likely to form.
Applicable Scene
Relative humidity is widely used in fields such as weather forecasting, agricultural planting, construction, environmental monitoring, precision manufacturing, and healthcare. In agriculture, properly controlling relative humidity helps prevent crop diseases and the breeding of greenhouse pests and diseases. In museums and cultural heritage preservation, relative humidity control is crucial for preserving organic materials such as paper, fabric, and wood products. In human comfort assessment, relative humidity, combined with temperature, determines the “perceived temperature,” directly affecting people’s subjective perception of heat and cold.
Pros: The greatest advantage of relative humidity is that it provides an intuitive and relatively uniform measure of air humidity, allowing comparisons to be made as a percentage across a wide range of temperature environments. Furthermore, relative humidity can be quickly measured using simple instruments such as hygrometers and electronic sensors, making it convenient for daily environmental monitoring and industrial control. Compared to indicators such as absolute humidity, RH is easier for non-specialists to understand and use, leading to its widespread adoption in public meteorological services.
Cons: Despite its universal applicability, relative humidity is essentially a relative quantity, highly dependent on the current air temperature. As temperatures rise, relative humidity decreases, even if the water vapor content remains constant, creating the illusion of dryness. Conversely, at low temperatures, relative humidity can be high even with minimal water vapor. Furthermore, relative humidity does not directly reflect the absolute water vapor content. Therefore, in scenarios requiring precise control of moisture content (such as industrial dehumidification and climate simulation), it must be used in conjunction with indicators such as dew point temperature or absolute humidity for a more accurate assessment.
Legend
1. Relative humidity.
2. Relative humidity formula.
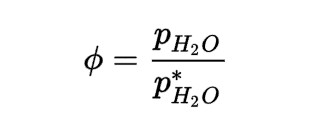
Related Article
Reference Link
https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relative_humidity
https://zoom.earth/maps/humidity/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/relative-humidity